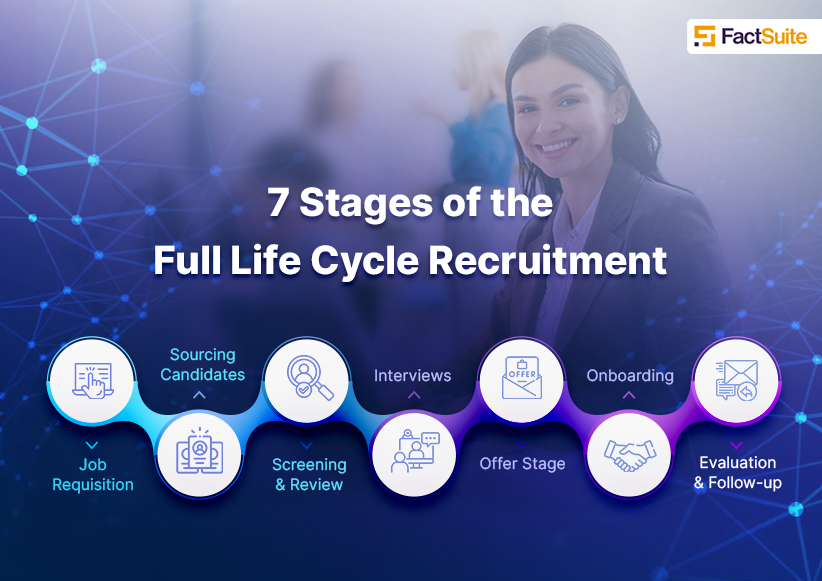
7 Stages of the Full Life Cycle Recruitment
In the realm of human resources, recruitment stands as a critical pillar, steering the course of organizational growth and success. Among the varied methodologies employed, the Full Life Cycle Recruitment approach emerges as a comprehensive framework encompassing seven pivotal stages. Let's delve into the intricacies of this process, exploring its essence, benefits, challenges, and key responsibilities.
Table of Contents
What is the Full Recruitment Life Cycle?
Who is Responsible for Conducting the Stages of the Full Life Recruitment Cycle?
- HR/Recruitment Team
- Hiring Managers
- Candidates
- External Partners/Agencies
- Collaborative Effort
7 Steps of the Full Life Cycle Recruiting Process
- Job Requisition
- Sourcing Candidates
- Screening and Review
- Interviews
- Offer Stage
- Onboarding
- Evaluation and Follow-up
Benefits of Full Cycle Recruiting
- Comprehensive Candidate Fit
- Reduced Time-to-Hire
- Enhanced Candidate Experience
- Cost Efficiency
- Improved Talent Pipeline
- Consistency and Compliance
- Higher Employee Retention
Challenges of Full Cycle Recruiting
- Resource Intensity
- Potential Bias
- Coordination Complexity
- Candidate Experience
- Skill Shortages
- Technological Adaptation
- Evolving Market Dynamics
Tools to Manage the Full Life Cycle Recruiting
- Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS)
- Job Boards and Recruitment Platforms
- Candidate Relationship Management (CRM) Software
- Video Interviewing Tools
- Pre-Employment Assessment Tools
- Onboarding Software
- HR Analytics and Reporting Tools
- AI-Powered Recruitment Tools
- Collaboration and Communication Tools
Leveraging the Full Recruitment Cycle
- Clear Job Requirement Definition
- Strategic Sourcing Channels
- Efficient Screening and Evaluation
- Seamless Interview Process
- Engaging Offer and Onboarding
- Continuous Process Refinement
- Embrace Technology Wisely
- Foster Collaboration Among Stakeholders
- Prioritize Candidate Experience
What is the Full Recruitment Life Cycle?
The Full Life Cycle Recruitment represents a systematic sequence of stages involved in acquiring top talent. It spans from the initial identification of a vacancy to onboarding the selected candidate. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring a seamless recruitment journey, aligning organizational needs with the best-fit candidates.
Who is Responsible for Conducting the Stages of the Full Life Recruitment Cycle?
The Full Life Cycle Recruitment process involves a collaborative effort among various stakeholders, each shouldering specific responsibilities crucial to the success of the recruitment journey.
HR/Recruitment Team:
At the helm of the Full Life Cycle Recruitment process stands the HR or Recruitment team. Their primary responsibility encompasses overseeing and orchestrating the entire recruitment spectrum. They steer the process from job requisition to candidate onboarding, ensuring adherence to the defined strategy, policies, and compliance requirements.
Hiring Managers:
Collaboration between the HR team and Hiring Managers is pivotal. These managers play a pivotal role in the initial stages by defining job requirements, delineating the necessary skills and qualifications, and actively participating in candidate evaluation and selection. Their insight into the role's intricacies aids in identifying the best-fit candidates.
Candidates:
Candidates themselves contribute significantly to the smooth execution of the recruitment stages. Their responsibility lies in providing accurate and comprehensive information, participating actively in the interview process, and adhering to the guidelines outlined by the organization.
External Partners/Agencies:
In some instances, organizations may engage external recruitment agencies or partners. These entities support the recruitment process by sourcing candidates, conducting initial screenings, and presenting qualified individuals for consideration. Collaboration with these partners demands clear communication and alignment with the organization's goals and values.
Collaborative Effort:
Successful Full Life Cycle Recruitment hinges on a synchronized effort among these stakeholders. Communication, cooperation, and shared accountability are imperative to navigate through each stage seamlessly, ensuring the selection of the most suitable candidate for the vacant position.
In essence, while the HR/Recruitment team takes the lead, a cohesive collaboration among Hiring Managers, candidates, and potentially external partners shapes an effective Full Life Cycle Recruitment strategy, culminating in securing the best talent for organizational growth.
7 Steps of the Full Life Cycle Recruiting Process
Recruiting top talent involves a strategic process comprising seven essential steps. Understanding these stages is key to successful talent acquisition.
1. Job Requisition:
The process kicks off with defining the job requirements. Hiring managers collaborate with HR to outline the role's responsibilities, skills needed, and qualifications required for potential candidates.
2. Sourcing Candidates:
Recruiters actively seek potential candidates through various channels like job boards, social media platforms, referrals, and networking events. This stage aims to gather a diverse pool of applicants.
3. Screening and Review:
Received resumes are thoroughly reviewed to shortlist candidates meeting the job criteria. Initial screenings, assessments, and evaluations help filter out unsuitable applicants.
4. Interviews:
Qualified candidates proceed to the interview stage. This often involves multiple rounds, including technical assessments and cultural fit discussions, providing insights into the candidate's suitability for the role and the organization.
5. Offer Stage:
After selecting the most suitable candidate, an offer is extended. This stage involves negotiating terms, salary, benefits, and other employment details.
6. Onboarding:
Once the candidate accepts the offer, the onboarding process begins. This step ensures a smooth transition for the new hire, integrating them into the company's culture, processes, and team dynamics.
7. Evaluation and Follow-up:
Continuous assessment of the recruitment process is vital for improvement. Feedback from candidates, hiring managers, and HR helps refine future recruitment strategies.
Understanding these seven steps and effectively managing each stage is essential for organizations seeking to attract, select, and onboard the right talent for their teams.
Benefits of Full Cycle Recruiting
Implementing a Full Cycle Recruiting approach offers several advantages that significantly impact an organization's talent acquisition strategy.
1. Comprehensive Candidate Fit:
Full Cycle Recruiting ensures a thorough assessment of candidates against job requirements. This holistic approach results in better alignment between the candidate's skills, experience, and the organization's needs, leading to higher-quality hires.
2. Reduced Time-to-Hire:
Managing the entire recruitment process efficiently minimizes the time taken to fill vacant positions. From sourcing to onboarding, streamlining each stage speeds up the hiring process without compromising quality.
3. Enhanced Candidate Experience:
A well-structured recruitment process positively influences the candidate's perception of the organization. A positive experience, regardless of the outcome, contributes to a strong employer brand, attracting top talent in the future.
4. Cost Efficiency:
Efficient recruitment strategies save resources. By reducing the time and effort spent on hiring and training due to better candidate fit, organizations can optimize their budget allocation.
5. Improved Talent Pipeline:
Full Cycle Recruitment establishes a continuous relationship with potential candidates. Even if they are not selected initially, maintaining a positive interaction can create a talent pool for future job openings, reducing sourcing time for subsequent vacancies.
6. Consistency and Compliance:
Following a structured recruitment process ensures consistency and adherence to legal and regulatory standards. This minimizes the risk of biases and discrimination while ensuring compliance with labor laws.
7. Higher Employee Retention:
A robust recruitment process that aligns candidates' skills and organizational culture often results in better job satisfaction and higher retention rates among new hires.
Embracing the Full Cycle Recruiting methodology provides organizations with a competitive edge by optimizing the talent acquisition process, securing the right talent, and fostering long-term success.
Challenges of Full Cycle Recruiting
While Full Cycle Recruiting offers numerous benefits, challenges of Full Cycle Recruiting must be navigated by organizations to optimize their recruitment strategies.
1. Resource Intensity:
Managing the entire recruitment process demands considerable time, effort, and resources. Balancing multiple stages, from sourcing to onboarding, can strain HR teams and other stakeholders involved in the process.
2. Potential Bias:
Throughout the stages of recruitment, unconscious biases might inadvertently influence decision-making. This bias could impact candidate evaluation, leading to overlooking qualified candidates or favoring certain demographics, undermining diversity and inclusion efforts.
3. Coordination Complexity:
Coordinating various stakeholders, including hiring managers, candidates, and external partners, can be intricate. Aligning schedules, maintaining communication, and ensuring everyone adheres to the recruitment process can pose logistical challenges.
4. Candidate Experience:
A lengthy or convoluted recruitment process can negatively impact the candidate experience, posing as one of the critical challenges of Full Cycle Recruiting. Lengthy waiting periods or unclear communication might deter potential candidates, harming the organization's employer brand.
5. Skill Shortages:
In certain industries or for specialized roles, finding candidates with the required skills can be challenging. This scarcity amplifies the competition among employers, making talent acquisition even more daunting.
6. Technological Adaptation:
Implementing and managing recruitment technologies and tools demands adaptation. Ensuring that these tools integrate seamlessly into the recruitment process while providing accurate insights can be a hurdle for some organizations.
7. Evolving Market Dynamics:
Market fluctuations, economic changes, or industry shifts can influence talent availability and job market dynamics. Keeping abreast of these changes and adjusting recruitment strategies accordingly poses a constant challenge.
Navigating these challenges demands a proactive approach, emphasizing continuous improvement, adapting to market changes, embracing diversity and inclusion, and leveraging technology to streamline processes while mitigating biases. Addressing these challenges of Full Cycle Recruiting strategically ensures a more effective Full Cycle Recruitment process.
Tools to Manage the Full Life Cycle Recruiting
The recruitment landscape has evolved, offering a plethora of tools and technologies designed to streamline and optimize the entire recruitment process. Leveraging these tools helps in effectively managing each stage of the Full Life Cycle Recruiting process.
1. Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS):
ATS platforms centralize the recruitment process, managing candidate data, job postings, and communication. These systems automate tasks like resume parsing, candidate tracking, and interview scheduling, enhancing efficiency.
2. Job Boards and Recruitment Platforms:
Online job boards and specialized recruitment platforms facilitate reaching a broader candidate pool. Platforms like LinkedIn, Indeed, or Glassdoor enable job postings, candidate sourcing, and networking with potential candidates.
3. Candidate Relationship Management (CRM) Software:
CRM systems aid in building and nurturing candidate relationships. They track interactions, automate communication, and maintain candidate databases for future opportunities.
4. Video Interviewing Tools:
Remote or virtual interviews have become commonplace. Video interviewing tools like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or specialized interview platforms streamline the interview process, allowing remote assessment of candidates.
5. Pre-Employment Assessment Tools:
Assessment platforms offer various tests and simulations to evaluate candidates' skills, cognitive abilities, and personality traits, aiding in identifying the best-fit candidates.
6. Onboarding Software:
Dedicated onboarding tools streamline the induction process for new hires. These platforms facilitate paperwork, orientation, and training, ensuring a smooth transition into the organization.
7. HR Analytics and Reporting Tools:
Analytics tools provide insights into recruitment metrics, offering data-driven assessments of the recruitment process's efficiency, candidate sourcing channels, and time-to-hire metrics.
8. AI-Powered Recruitment Tools:
Artificial Intelligence tools assist in automating tasks like resume screening, candidate matching, and predictive analysis, optimizing the recruitment process and reducing manual effort.
9. Collaboration and Communication Tools:
Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or project management platforms foster seamless communication and collaboration among hiring teams, ensuring effective coordination during the recruitment process.
Utilizing these tools in conjunction with a structured approach amplifies the effectiveness of Full Life Cycle Recruiting. Customizing the toolset based on organizational needs and the specific requirements of each stage can significantly enhance recruitment efficiency.
Leveraging the Full Recruitment Cycle
Harnessing the potential of the Full Recruitment Cycle is instrumental in acquiring top-tier talent and fostering organizational growth. Understanding how to maximize its impact is key to optimizing the recruitment process.
1. Clear Job Requirement Definition:
Begin by meticulously defining job requirements in collaboration with hiring managers. This clarity sets the stage for effectively sourcing and assessing candidates who align with the role.
2. Strategic Sourcing Channels:
Utilize diverse sourcing channels such as job boards, social media, networking, and employee referrals. Employing a multifaceted approach widens the candidate pool, enhancing the chances of finding the ideal fit.
3. Efficient Screening and Evaluation:
Implement robust screening methods aligned with job specifications. Employ assessments, interviews, and evaluations that effectively gauge candidate skills, experience, and cultural fit.
4. Seamless Interview Process:
Craft an interview process that not only assesses technical competencies but also evaluates cultural alignment. Engage candidates in meaningful discussions to ascertain their suitability for the role and organizational ethos.
5. Engaging Offer and Onboarding:
Present compelling offers promptly, emphasizing the value proposition. Streamline the onboarding process to ensure a smooth transition, integrating new hires seamlessly into the company culture.
6. Continuous Process Refinement:
Regularly evaluate and refine the recruitment process. Gather feedback from stakeholders, analyze recruitment metrics, and adapt strategies to improve efficiency and candidate experience.
7. Embrace Technology Wisely:
Leverage recruitment tools and technologies strategically. Adopt applicant tracking systems, AI-driven tools, and communication platforms to streamline processes while mitigating biases and enhancing candidate engagement.
8. Foster Collaboration Among Stakeholders:
Encourage collaboration between HR, hiring managers, and external partners. Clear communication, shared responsibilities, and synchronized efforts are crucial for a successful recruitment cycle.
9. Prioritize Candidate Experience:
Prioritize candidate experience throughout the recruitment journey. Timely communication, transparency, and a positive interaction leave a lasting impression, impacting the employer brand positively.
Leveraging the Full Recruitment Cycle involves a strategic, collaborative, and iterative approach. By optimizing each stage, organizations can attract, select, and retain top talent, thereby propelling sustained growth and success.